1ink Repeated Systematic Sampling With N10 Again N60
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a statistical method that researchers utilise to zero downwards on the desired population they want to research. Researchers calculate the sampling interval by dividing the entire population size by the desired sample size. Systematic sampling is an extended implementation of probability sampling in which each fellow member of the group is selected at regular periods to form a sample.
Systematic sampling definition
Systematic sampling is defined as a probability sampling method where the researcher chooses elements from a target population by selecting a random starting betoken and selects sample members after a stock-still 'sampling interval.'
Select your respondents
For example, in schoolhouse, while selecting the helm of a sports squad, near of our coaches asked us to call out numbers such as i-five (1-northward) and the students with a random number decided past the coach. For instance, iii would be called out to be the captains of different teams. It is a non-stressful option process for both the bus and the players. There'southward an equal opportunity for every member of a population to be selected using this sampling technique.
What are the steps to form a sample using the systematic sampling technique?
Here are the steps to form a systematic sample:
Footstep i: Develop a defined structural audience to first working on the sampling aspect.
Step two: As a researcher, effigy out the platonic size of the sample, i.e., how many people from the entire population to cull to be a office of the sample.
Step three: In one case you decide the sample size, assign a number to every member of the sample.
Step four: Define the interval of this sample. This volition exist the standard distance between the elements.
For example, the sample interval should exist 10, which is the result of the partition of 5000 (N= size of the population) and 500 (n=size of the sample).
Systematic Sampling Formula for interval (i) = North/n = 5000/500 = x
Pace five: Select the members who fit the criteria which in this case will exist 1 in 10 individuals.
Footstep six: Randomly cull the starting member (r) of the sample and add the interval to the random number to continue adding members in the sample. r, r+i, r+2i, etc. will be the elements of the sample.
How systematic sampling works
When yous are sampling, ensure you represent the population fairly. Systematic sampling is a symmetrical process where the researcher chooses the samples later on a specifically defined interval. Sampling like this leaves the researcher no room for bias regarding choosing the sample. To empathize how systematic sampling exactly works, take the case of the gym class where the instructor asks the students to line upward and asks every tertiary person to step out of the line. Here, the instructor has no influence over choosing the samples and can accurately represent the class.
Systematic sampling example
For instance, if a local NGO is seeking to grade a systematic sample of 500 volunteers from a population of 5000, they tin can select every 10th person in the population to build a sample systematically.
What are the types of systematic sampling?
Here are the types of systematic sampling:
- Systematic random sampling
- Linear systematic sampling
- Circular systematic sampling
Allow's take a closer look at these sampling techniques.
Systematic random sampling:
Systematic random sampling is a method to select samples at a item preset interval. As a researcher, select a random starting betoken betwixt ane and the sampling interval. Beneath are the instance steps to set up a systematic random sample:
- Commencement, calculate and fix the sampling interval. (The number of elements in the population divided by the number of elements needed for the sample.)
- Choose a random starting signal between 1 and the sampling interval.
- Lastly, repeat the sampling interval to choose subsequent elements.
Linear systematic sampling:
Linear systematic sampling is a systematic sampling method where samples aren't repeated at the end and 'n' units are selected to exist a part of a sample having 'N' population units. Rather than selecting these 'north' units of a sample randomly, a researcher tin can apply a skip logic to select these. It follows a linear path and so stops at the end of a particular population.
This sampling or skip interval (k) = Northward (total population units)/n (sample size)
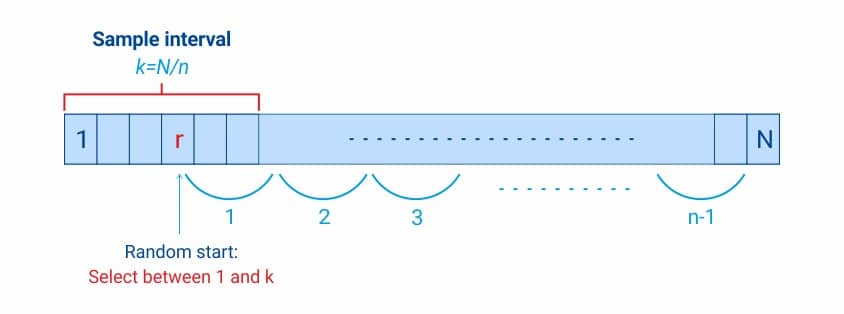
How is a Linear systematic sample selected?
- Adapt the unabridged population in a classified sequence.
- Select the sample size (n)
- Calculate sampling interval (k) = N/northward
- Select a random number between one to k (including grand)
- Add the sampling interval (k) to the chosen random number to add the side by side member to a sample and echo this procedure to add remaining members of the sample.
- In case g isn't an integer, you can select the closest integer to N/n.
Round systematic sampling:
In round systematic sampling, a sample starts again from the same point once once more after catastrophe; thus, the name. For instance, if North = 7 and n = 2, yard=3.5. There are two likely ways to form sample:
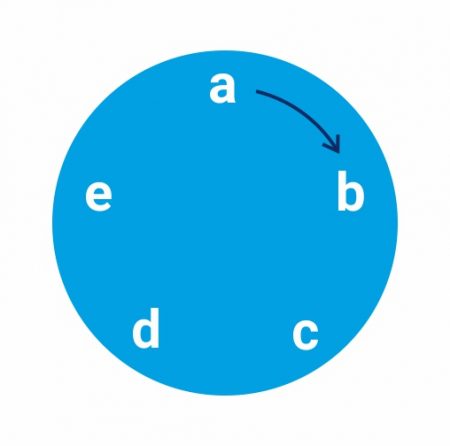
- If we consider k=3, the samples will be – ad, exist, ca, db and ec.
- If nosotros consider k=4, the samples will be – ae, ba, cb, dc and ed.
How is a round systematic sample selected?
- Calculate sampling interval (k) = N/n. (If North = 11 and n = 2, then k is taken as 5 and not 6)
- Start randomly betwixt 1 to N
- Create samples by skipping through k units every fourth dimension until yous select members of the entire population.
- In the instance of this method, there will be North number of samples, dissimilar k samples in the linear systematic sampling method.
Difference between linear systematic sampling and round systematic sampling:
Hither is the difference betwixt linear systematic sampling and circular systematic sampling.
| Linear Systematic Sampling | Circular Systematic Sampling |
| Create samples = thousand (sampling interval) | Create samples = N (full population) |
| The start and endpoints of this sample are distinct. | Information technology restarts from the showtime point one time the entire population is considered. |
| All sample units should be arranged in a linear manner prior to selection. | Elements will be arranged in a circular style. |
What are the advantages of systematic sampling?
Hither are the advantages of systematic sampling.
- It'south extremely unproblematic and user-friendly for the researchers to create, conduct, analyze samples.
- Every bit there's no need to number each member of a sample, information technology is meliorate for representing a population in a faster and simpler fashion.
- The samples created are based on precision in member selection and gratuitous from favoritism.
- In the other methods of probability sampling methods such as cluster sampling and stratified sampling or not-probability methods such as convenience sampling, in that location are chances of the clusters created to be highly biased which is avoided in systematic sampling equally the members are at a stock-still distance from one some other.
- The cistron of risk involved in this sampling method is extremely minimal.
- In case there are diverse members of a population, this sampling technique can exist benign because of the even distribution of members to form a sample.
Other probability sampling techniques like cluster sampling and stratified random sampling can be very unorganized and challenging due to which researchers and statisticians have turned to methods like systematic sampling or simple random sampling for amend sampling results. It consumes the to the lowest degree time as it requires a pick of sample size and identification of the starting point for this sample, which needs to exist connected at regular intervals to form a sample.
Select your respondents
When to use systematic sampling?
Let'southward take an instance where you desire to form a sample of 500 individuals out of a population of 5000; you'd accept to number every person in the population.
Once the numbering is done, the researcher can select a number randomly, for instance, 5. The fifth private will be the offset to be a part of the systematic sample. Subsequently that, the tenth member will be added into the sample, then on so along (15th, 25th, 35, 45th, and members till 4995).
Here are 4 other situations of when to employ Systematic Sampling:
- Upkeep restrictions: In comparison to other sampling methods similar simple random sampling, this sampling technique is more suitable for conditions where there are upkeep restrictions and also the extremely uncomplicated accomplishment of the report.
- Simple implementation: As systematic sampling depends on the divers sampling intervals to decide the sample, it becomes simple for the researchers and statisticians to manage samples with more respondents. This is considering the fourth dimension invested in creating samples is minimal, and the toll spent is also restricted due to the periodic nature of systematic sampling.
- Absence of information pattern: There are specific information that don't accept an arrangement in place. This information can be analyzed in an unbiased manner, using systematic sampling.
- Low risk of information manipulation in research: Information technology is highly productive while researching a broad subject, especially when in that location's a negligible risk of data manipulation.
Sampling with QuestionPro Audition
QuestionPro Audience has a global sample of 22 1000000+ survey respondents who are double-opted and mobile-fix to participate in all levels of market research and brand research. Demand niche panelists like gamers, building contractors, direct get in touch with our niche panelists.
Source: https://www.questionpro.com/blog/systematic-sampling/
Post a Comment for "1ink Repeated Systematic Sampling With N10 Again N60"